Schedules Overview
Schedules Basics
Schedules allow to configure automated procedures in evalink talos to behave differently depending on the timetable of an entity. Schedules can be created for entities that exist:
-
on the site level (a site schedule is required)
-
on the site group level (a site group schedule is required)
-
on the Company level (a global schedule is required)
Schedule States
A schedule defines the following timespans:
-
the activity periods (for example, the site working hours) – during these periods a schedule is said to be in Active state
-
the inactivity periods (for example, the periods outside the site working hours) – during these periods a schedule is said to be in Inactive state
A number of automated procedures can be based on a schedule in evalink talos. Examples include:
-
triggering alarms on schedule state transitions (Active to Inactive and vice versa)
-
making decisions in a workflow after checking the state of a schedule
When an emergency occurs, a workflow can, for example
-
through the site opening hours – inform the in-house personnel
-
through the closed hours – inform the police or an intervention team
-
-
setting the availability of a contact based on a schedule, to ensure, for example, that a contact is not being approached outside their working hours
Schedule Access Permissions
Only Administrator and Manager can create schedules.
Operator cannot create or delete schedules, but has certain limited permissions for schedule editing.
The operations available with the current user permissions (Administrator, Manager, or Operator) are described in section Manage Schedules.
All users, including Operator Minimal, can add, edit, or delete the entries in a schedule within the Add Schedule Entry step, when processing a Manual Workflow that contains this step.
For details, see section View a Schedule > View Schedule Details when Processing an Alarm.
Configuring Schedules
Schedules can be created on the site, site group, and global levels.
Schedules created on higher levels (for example, on the global or on the site group level) can be used by site-level workflows and contacts.
For example, when creating a workflow for a site, Administrator or Manager can include a Check Schedule step (see section Automated Steps > Automated Decisions > Check Schedule in Workflow Reference > Workflow Step Reference) in the workflow. This step can be configured to check a site schedule, a schedule of the containing site group, or a global schedule.
When creating a schedule, Administrator or Manager typically:
- Configures a regular working week schedule – creates the main schedule
The main schedule for the working week consists of recurring entries of Day of Week type.
-
Specifies the exceptions for particular days of the year when the schedule is different, by
-
creating individual schedule entries for the concerned dates or date spans
OR
-
adding and configuring Special Days (see section Special Days)
OR
-
including other schedules into the current schedule (see section Included Schedules)
-
Buffer Times
It is possible to set buffer times for schedule start and end time.
Buffer time allows to trigger schedule activation / deactivation alarms (see section Schedule States) earlier or later than the schedule start / end time for the specified time period. For example, if the schedule start time is 9:00, and the buffer time for start time is set to 5 minutes, a schedule activation alarm is triggered at 8:55.
Buffer times shift accordingly the alarms triggered by all automated activities that rely on a schedule - for example, Status Rules (see section Work with Site Statuses > Statuses Overview > Status Rules).
This helps eliminate false alarms occurring due to the human factor – for example, early openings or late closings of the office by the personnel.
Buffer times can be set to:
- positive values
- negative values
- zero (the default option)
A positive buffer time is applied outside the schedule hours, allowing to tolerate, for example, early disarms and late arms.
A negative buffer time is applied inside the schedule hours, allowing to tolerate, on the opposite, late disarms and early arms.
Either a positive or a negative buffer can be applied to one time point (for example, to schedule start). To configure a setup that wraps a buffer around a time point, two schedules are required.
You can set buffer times for a schedule:
-
during the creation of a schedule, see section Manage Schedules > Create a Schedule
-
for an existing schedule – see section More Operations with Schedules > Check and Edit the Schedule Buffer Times
Included Schedules
evalink talos allows to include one schedule into another. Typically, global or site group-level schedules are included into site schedules in order to specify the exceptions from the regular working hours. The use of included schedules is described in section Getting Started with Schedules: a Summary.
If some entries in the main and an included schedule conflict with each other, the rules described in section Advanced Topics > Schedule Hours Priority in Case of a Conflict apply.
The buffer times (see section Schedules Overview > Buffer Times) and the time zone of the included schedule are ignored.
For instructions on including a schedule, see section Manage Schedules > Include Another Schedule into a Schedule.
Special Days
Special Days are used to specify the particular days of the year when the schedule differs.
Only Administrator and Manager can create Special Days.
A Special Day is a date placeholder that is created on a global level. The working hours for a Special Day are filled in when the Special Day is added to a particular schedule.
When added to a schedule, a Special Day is displayed as one of the schedule entries, see the figures in section View a Schedule > List View.
For information on configuring a Special Day, see section Manage Schedules > Create a Special Day and Add It to a Schedule.
Special Days Usage Tips
Special days can be added:
-
to site schedules directly
OR
-
to higher-level schedules (global or site group schedules), which are then included into site schedules
See below to know when it is convenient to use each of these options.
When to Add a Special Day to a Site Schedule Directly
It is convenient to add Special Days directly into the site schedule for the days of the year that:
-
are not bank holidays
-
may have different working hours on different sites
An example of such a Special Day is Christmas Eve.
A Special Day is created, added to a site schedule, and site-specific hours are configured for it.
When to Add a Special Day within an Included Schedule
For days off that are acknowledged by many sites, it is convenient to create Special Days and add these Special Days to higher-level schedules first, in order to configure the hours for them. In most cases, the hours would be 00:00-00:00, see section Advanced Topics > Schedule Entries Time Format.
By higher-level schedules, the following schedules are meant:
-
global schedules – can be used for bank holidays, for example, the Swiss National Day (August 1)
-
site group schedules – can be used for common days off, for example, the industry-specific maintenance days
These higher-level schedules can then be included into site-level schedules.
It is considered a good practice to create a separate global schedule for the bank holidays of each country and each administrative unit inside the country in which your sites are located. For example, if your sites operate in several cantons in Switzerland, it would be convenient to
-
Create a global schedule for Swiss holidays
-
Create a separate global schedule for the holidays of each Swiss canton that is concerned
-
Include in each site schedule at least this pair of global schedules:
-
the generic Swiss holidays schedule
-
the holiday schedule for the canton in which the site headquarters are located
-
Why Special Days
In global or site group schedules, exceptions from the regular schedule can be added as ordinary Date entries (see section Manage Schedules > Schedule Entry Types), but it is recommended to add them as Special Days. Adding them as Special Days has the following advantages:
-
a Special Day has a name specified for it, this makes the schedule more transparent
-
a Special Day is a recurring entry, which means that evalink talos automatically re-applies the Special Day every year, with little or no maintenance effort from Administrator or Manager
When configuring a Special Day, you can
-
attach it strictly to a certain date
OR
-
set it as an entry with a floating date, to address cases like the first Wednesday of March
evalink talos highlights the expired Special Days with floating dates, prompting to select the date for the upcoming year. For details, see section Manage Schedules > Create a Special Day.
-
Schedule Roles
Sites can have different business hours, different exceptions from those (such as company-specific days-off) and may operate in different time zones.
A Schedule Role is a placeholder that, when used in higher-level workflows (site group or global workflows), resolves to a particular schedule relevant to the site. As opposed to using a constant schedule, using a Schedule Role allows to process similar alarms occurring on different sites via the same workflow and still be able to check or edit the schedule of a particular site.
For general information about evalink talos roles, see section Advanced Features in evalink talos > Use of Roles.
A Schedule Role is created on a global level, and is then assigned to a particular schedule on the site, site group, or on the global level.
When a Schedule Role is assigned to schedule on different levels of hierarchy (site, site group, or Company), a workflow will first try to resolve the Schedule Role on the site level. If the current Schedule Role is not assigned on the site level, the workflow goes sequentially upwards in hierarchy until it resolves the role. For more detail, see section Advanced Features in evalink talos > Use of Roles > How a Role Is Applied.
For example, we have a Schedule Role Working hours. We have a global workflow that checks this Schedule Role whenever an alarm of a certain type (for example, the Disarm signal) arrives. The workflow invokes an action if the current time is outside the site working hours, and performs no action otherwise.
On Site A, the Working hours role is assigned to a schedule Mon-Fri 9:00-19:00, on Site B – to a schedule Mon-Sun 5:00-24:00. If a Disarm is signalled on Site A at 8:00 on Saturday, when the site should be Armed, it triggers an action. If the same alarm arrives at the same time on Site B, which is normally in Disarmed state at this time, no action follows.
Only Administrator and Manager can create Schedule Roles.
A Schedule Role, if assigned, is displayed in a bubble in the upper-right part of the schedule page, see the figures in section View a Schedule > Schedule Page.
A Schedule Role typically represents a particular type of a schedule, for example, Cleaning hours, Working hours.
For information on configuring Schedule Roles, see section Advanced Topics > Create a Schedule Role and Assign It to a Schedule.
Getting Started with Schedules: a Summary
The figure below shows the order of actions recommended when starting to work with schedules:
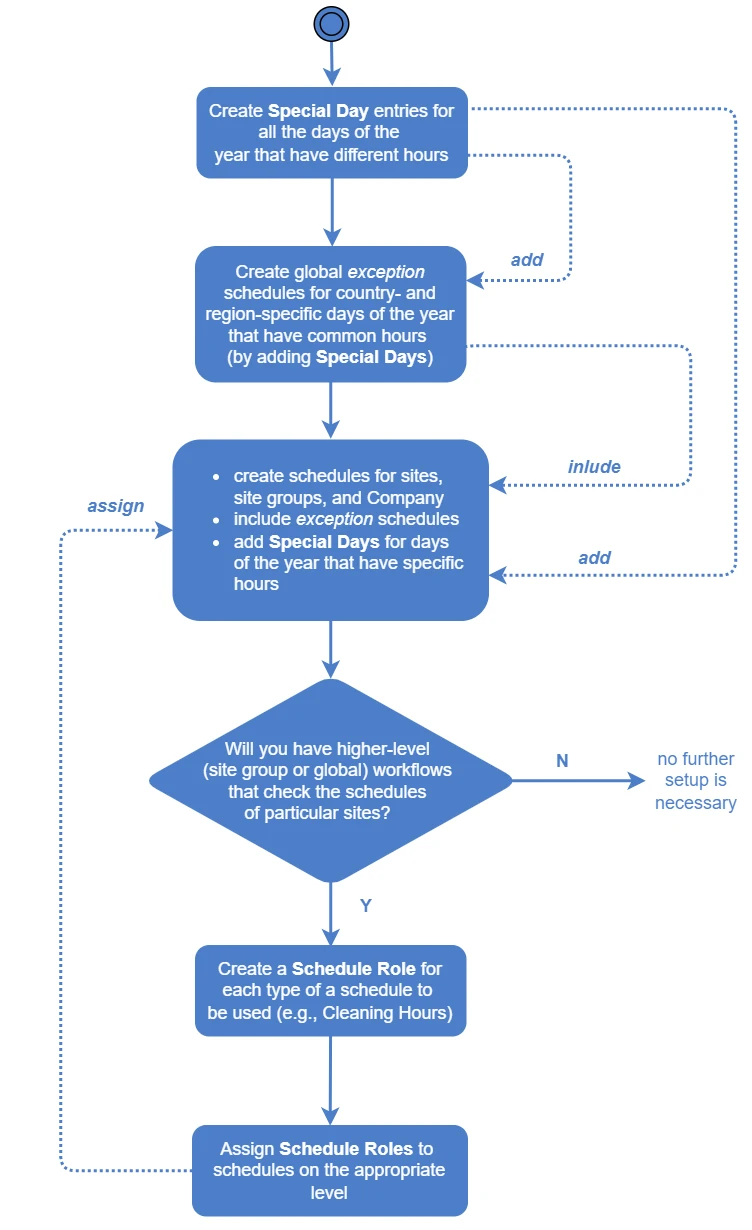
The setups shown on the figure can be configured by users with Administrator or Manager permissions.
-
Create Special Days for all specific days of the year in all countries and administrative units you need – for example, Swiss National Day, Easter, Hanukkah, etc.
You can create entries of Special Day type or of Date type for this purpose. Using Special Days is recommended.
See sections Special Days above and Manage Schedules > Create a Special Day and Add It to a Schedule for details about Special Days creation.
-
Configure global exception schedules for common days off / days with untypical hours:
a. Configure global Holiday schedules for the countries and administrative units you need - for example, Public Holidays Switzerland, Public Holidays Bern, etc.
Each of these schedules should contain Special Days only. Therefore, when creating such a schedule, select the Empty option in the Template field. See sections Manage Schedules > Create a Schedule for detailed instructions on creating a schedule.
infoYou can also configure schedules for site groups that have common exceptions from their regular schedules.
b. Add the Special Days (created on step 1) with common hours to these schedules, set the hours for these Special Days
See section Manage Schedules > Add a Special Day to a Schedule for instructions.
If some Special Days are likely to have diverse working hours across your sites, do not include them into exception schedules. It is better to include such Special Days into each site schedule directly. See section Schedules Overview > Special Days Usage Tips for an explanation.
-
Сreate site, site group, or global schedules (as necessary) and
a. Include the exception schedules (created on step 2) into these schedules
See section Manage Schedules > Include Another Schedule into a Schedule for instructions.
b. Add Special Days that have different hours to these schedules, specify the hours for these Special Days
See section and Manage Schedules > Create a Special Day and Add It to a Schedule.
-
To enable working with schedules from higher-level workflows (for example, checking a site schedule from a site group workflow), configure Schedule Roles
a. Create the necessary Schedule Roles
b. Assign Schedule Roles to schedules on the appropriate level
For information about the roles concept in evalink talos, see section Advanced Features in evalink talos > Use of Roles.
For details on working with Schedule Roles, see section Advanced Topics > Create a Schedule Role and Assign It to a Schedule.
 Link is copied
Link is copied