Workflows Basics
In this section, the term operator denotes an evalink talos user with any user role (Operator, Operator Minimal, Administrator, or Manager) who processes an alarm.
What is a Workflow
A workflow is a sequence of actions that are performed by evalink talos to process an alarm.
An alarm is always triggered for a certain site. Therefore, a workflow, though it can be created on different levels (site, site group, or global), is always executed for a particular site.
A workflow allows to implement a complete specialized end-to-end procedure for handling each type of alarm.
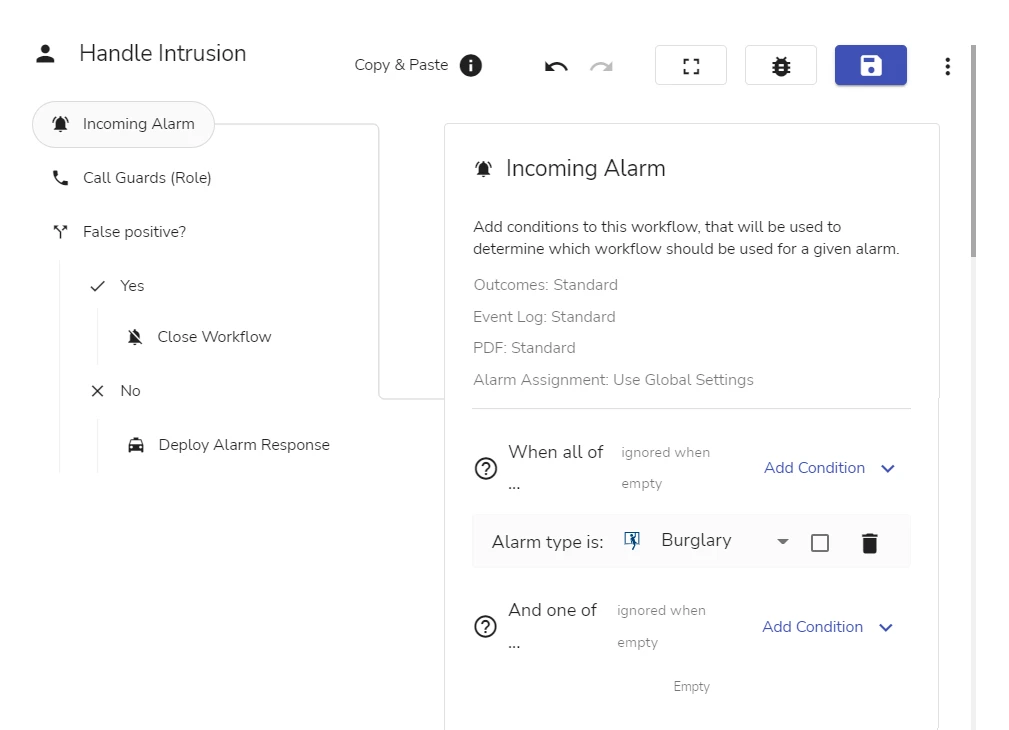
A workflow may include several conditional branches. Each branch can contain a separate action or a sequence of actions. For example, when a burglary alarm comes in, a workflow can be configured to verify the alarm by contacting a responsible person and, depending on the result:
- if the alarm is real, notify an intervention team
- if the alarm is a false positive, close the workflow
A workflow can also be configured to execute several branches (sequences of actions) in parallel.
The figure below shows a workflow opened in the workflow editor. The editor opens when you click on the workflow on the Workflows page. The workflow editor view (see below) is the same for site, site group, and global workflows.
The figure below shows the same workflow in the workflow processing view – a view that is available to the operator while processing the workflow:
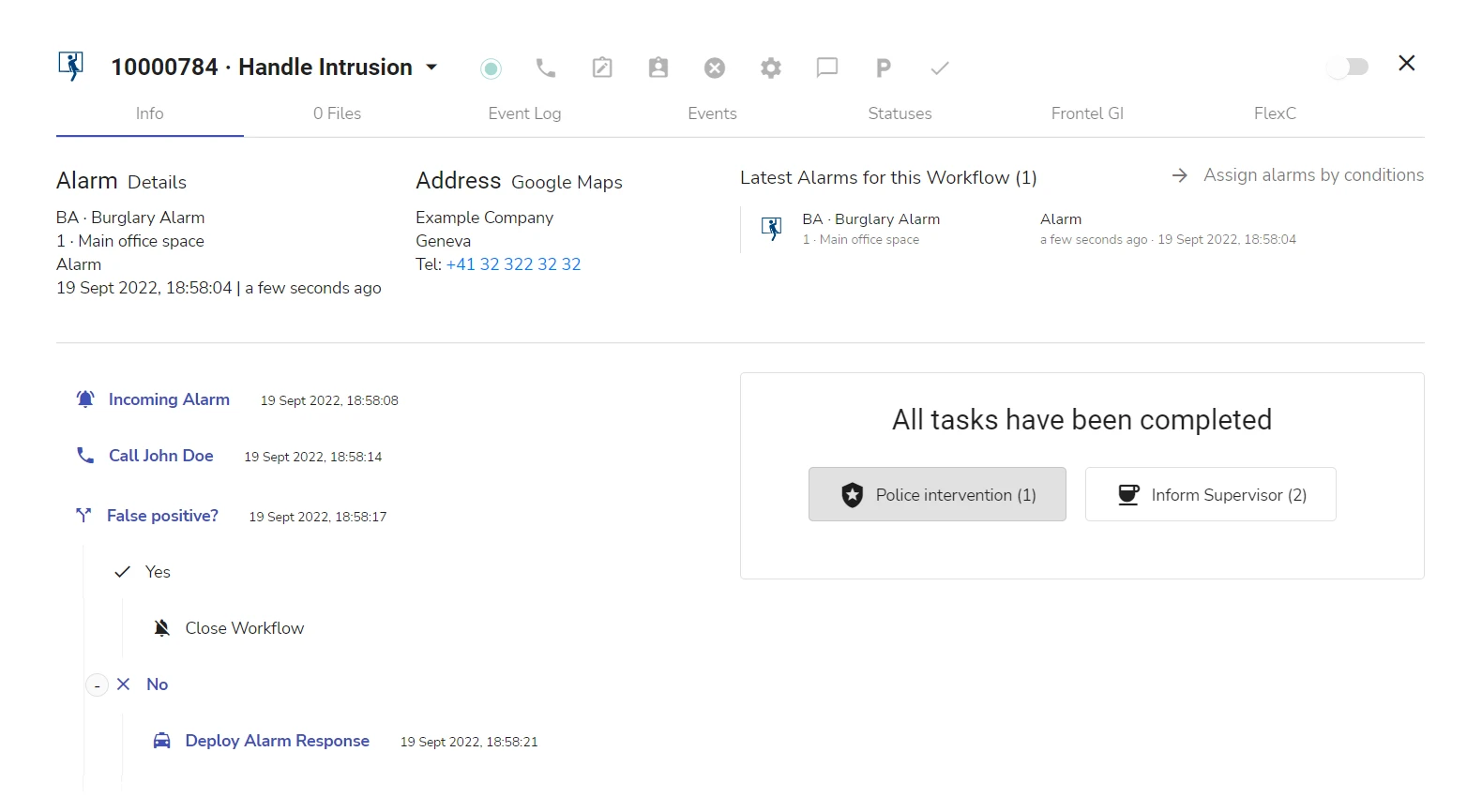
The actions highlighted in bold blue are the actions that were actually performed when the workflow followed the corresponding conditional branch.
As you can see from the two examples, when the workflow is executed, the Guards (Role) contact set in the workflow editor resolves to a particular site contact assigned with the Guards role (John Doe). For more details on how roles are used in workflows, see section Workflow Types > Site, Site Group, and Global Workflows > Use of Roles in Site Group and Global Workflows.
Only Administrator and Manager can create, edit or delete workflows.
Workflow Structure
A workflow consists of the following principal blocks:
- incoming conditions
- settings
- steps
Workflow Incoming Conditions
An alarm that is received for a site can be assigned to a certain workflow automatically, based on a set of incoming conditions that are configured for the workflow by Administrator or Manager. Incoming conditions may include, for example, an alarm code, the zone and / or partition, the alarm value (Alarm or Restore), a regular expression in the payload, etc., or any combination of such parameters.
The incoming conditions for a workflow are set in the Incoming Alarm step, see the figure below:
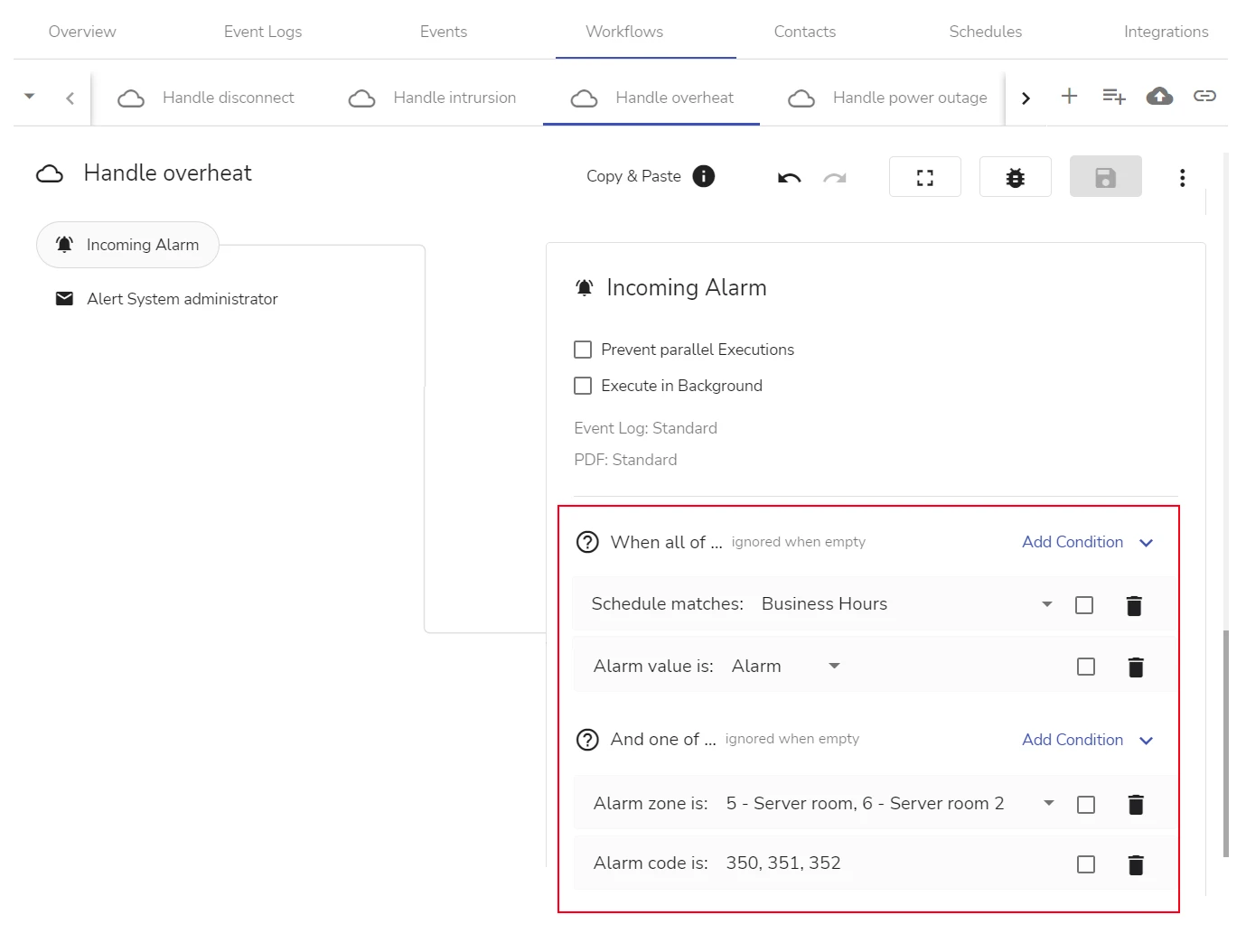
An alarm that satisfies the incoming conditions of the workflow above:
-
arrives during the hours of the Business Hours schedule
AND
-
has a value Alarm (alarms with Restore value do not trigger the current workflow)
AND either
- is triggered from zone 5 – Server room or from zone 6 – Server room 2
OR
- has one of these alarm codes: 350, 351, or 352
If one of the above condition combinations is fulfilled, an alarm is considered a match and triggers the workflow.
For details on setting incoming conditions for a workflow, see section Workflow Incoming Conditions and Workflow Comment > Workflow Incoming Conditions in Operations with a Workflow > Work with Workflows.
Workflow Settings
Workflows of different types (Manual, Automated, Managed, etc., see subsections in section Workflow Types) have different scopes of settings available.
The settings of a workflow define, for example:
- how the workflow event log is stored and distributed (see section Event Logging for Workflows > Event Logging Overview)
- if new alarms can be assigned to a workflow while it is in progress
- for Automated Workflows – see section Operations with a Workflow > Work with Workflow Settings > Prevent Parallel Executions Checkbox
- for Manual Workflows – see section Operations with a Workflow > Work with Workflow Settings > Alarm Assignment
- (for Automated Workflows only) if a workflow is a Foreground or a Background Workflow (see section Operations with a Workflow > Work with Workflow Settings > Execute in Background Checkbox)
- (for site group and global workflows only) the priority of a workflow when consuming alarms (see section Operations with a Workflow > Work with Workflow Settings > Override the Default Workflow Priority)
- (for Managed Workflows only) to which sites a workflow is linked (see section Operations with a Workflow > Work with Workflow Settings > Settings Specific for Managed Workflows)
For details on managing workflow event logging settings, see section Event Logging for Workflows. For details on managing other workflow settings, see section Operations with a Workflow > Work with Workflow Settings.
Workflow Steps
Each separate action performed in a workflow (for example, Close Workflow in the example above) is referred to as a workflow step.
The scope of steps available in a particular workflow depends on whether the workflow is Automated or Manual (see section Workflow Types > Manual and Automated Workflows).
Some workflow steps are available only when the corresponding integrations are configured in evalink talos. For example, the automated step Send Email becomes available only when the Email integration is enabled on the global Integrations page (Company > Integrations).
Manual and Automated Steps
A workflow can include, among other types of steps:
-
manual steps – steps that require some actions to be performed by the operator
Examples of manual steps are:
- Call Someone – calling a person
- Write a report – typing a report in free text format
-
automated steps – steps that don't require any human interaction and are performed by evalink talos automatically
Examples of automated steps are:
- Check Schedule – checking a schedule to understand if the alarm came during the schedule hours or not
- Send Email – sending an email notification, with a default or a customized message
For more information on the workflow steps available, see section Workflow Step Reference > Workflow Steps Overview and its subsections.
 Link is copied
Link is copied