Modbus
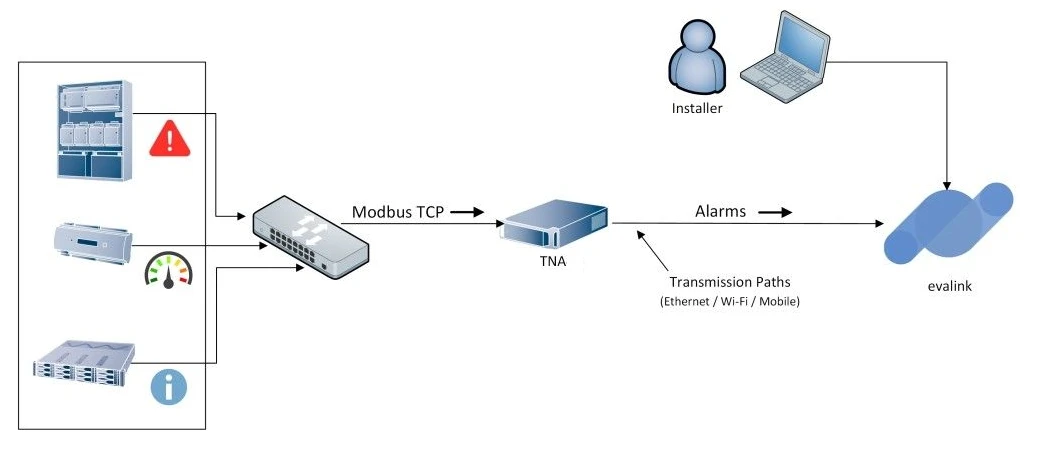
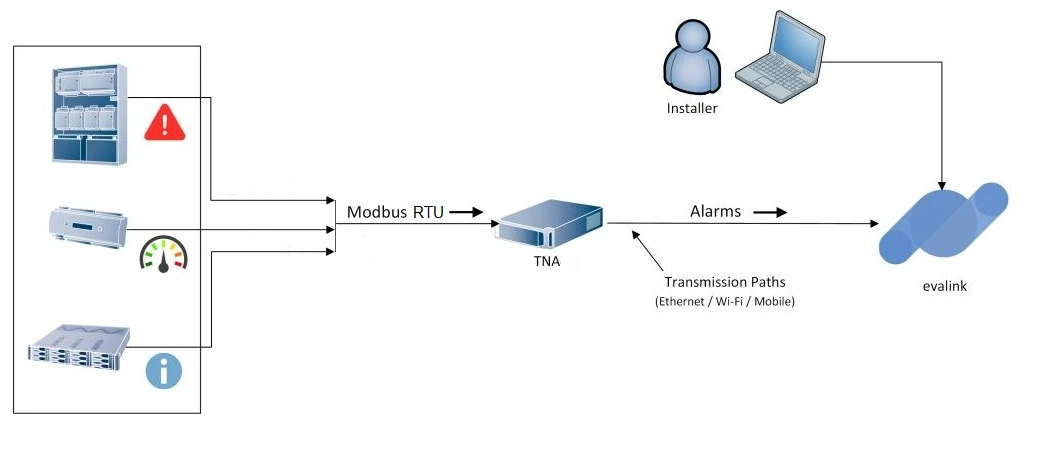
Modbus is an industrial data communications protocol intended for data exchanging between various devices. The protocol works over Serial (Modbus RTU) or over TCP (Modbus TCP).
The TNA starts a dedicated server after the Modbus integration is enabled. The server accepts incoming connections from devices, receives the alarms (also called coils), and forwards them to evalink talos.
Modbus TCP
Modbus RTU
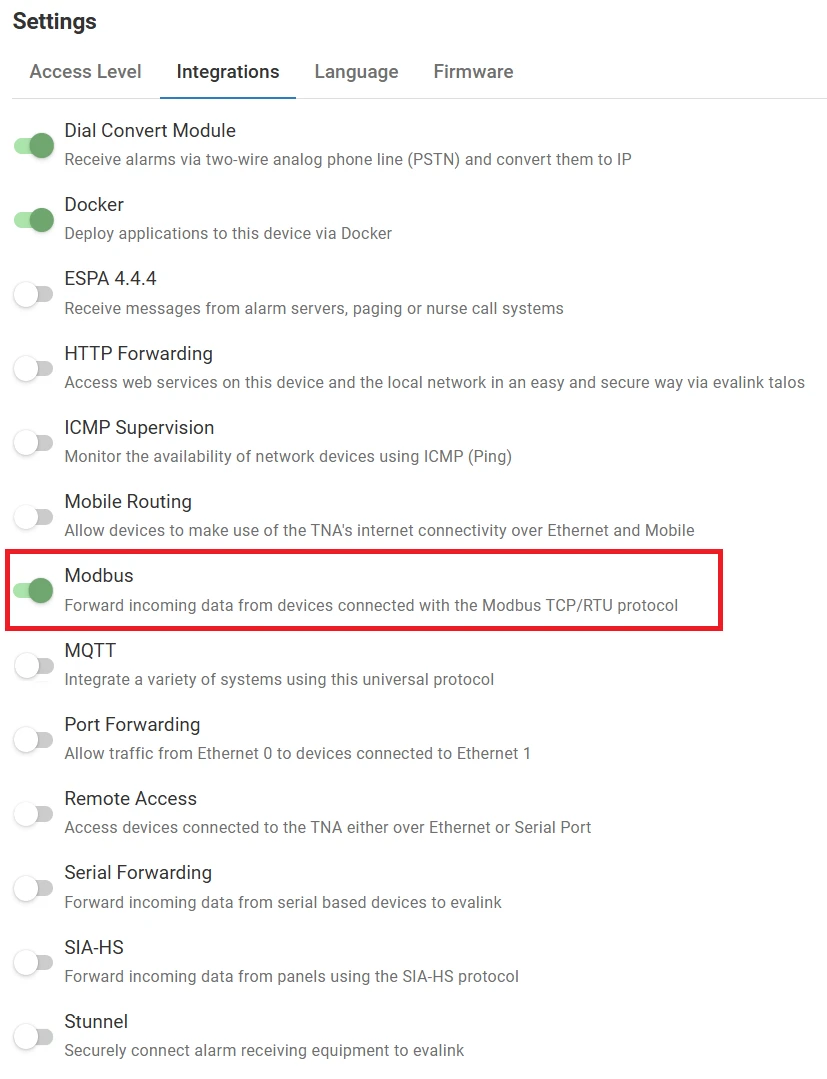
Enable Modbus on the TNA Web Server
Access level 4 is required to enable or disable the Modbus integration.
To enable the Modbus integration, do the following:
-
On the TNA Web Server, navigate to Settings > Integrations from the top right corner of the page
-
From the list of integrations, search for Modbus and toggle it
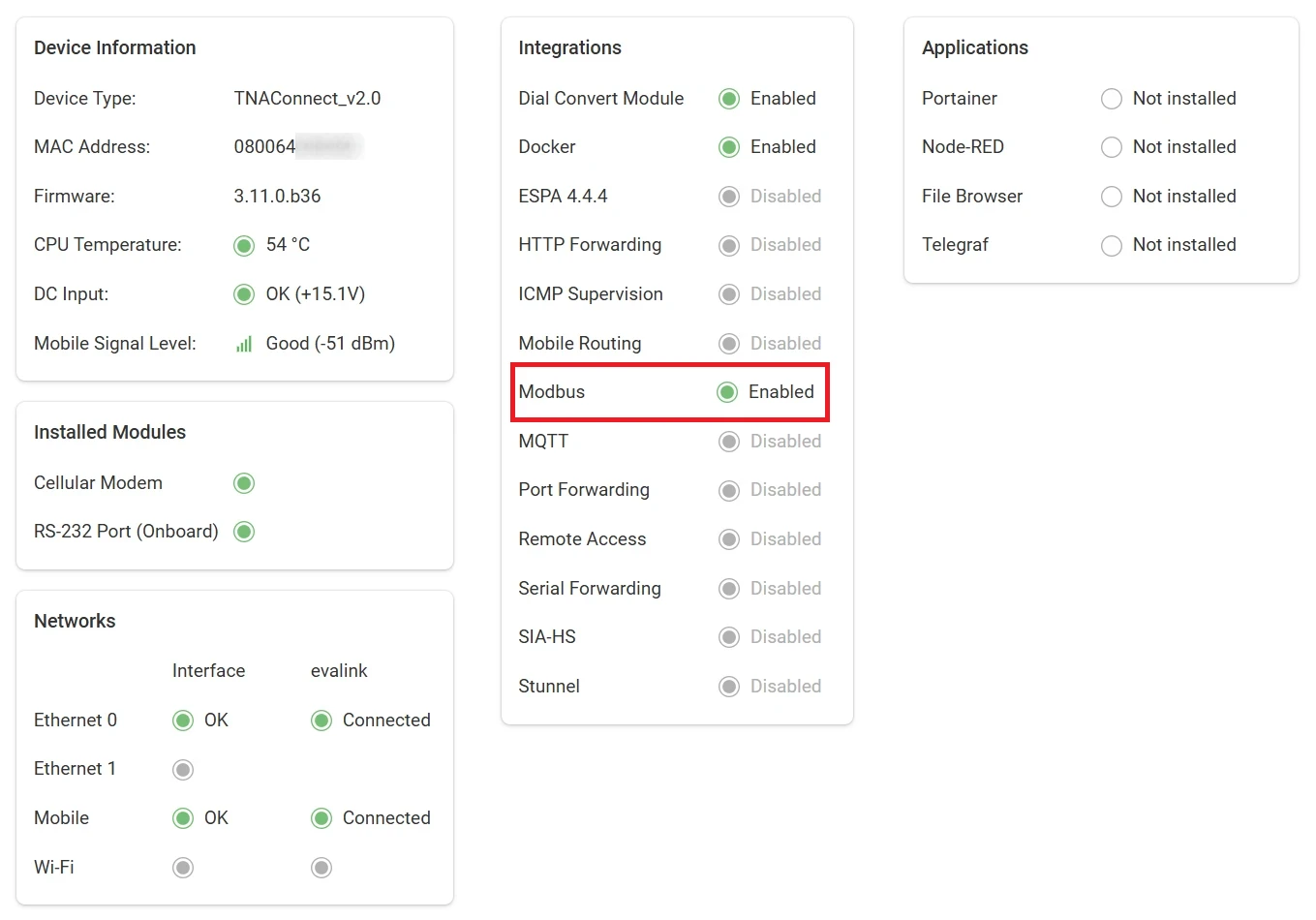
Once the Modbus integration is enabled, you can find it under Integrations on the top navigation menu.
The status is also reflected on the Integrations section of the Home page.
Configure Modbus
Access level 3 or above is required to configure Modbus.
To configure Modbus parameters, do the following:
- On the TNA Web Server, click on Integrations from the top navigation menu and choose
Modbus
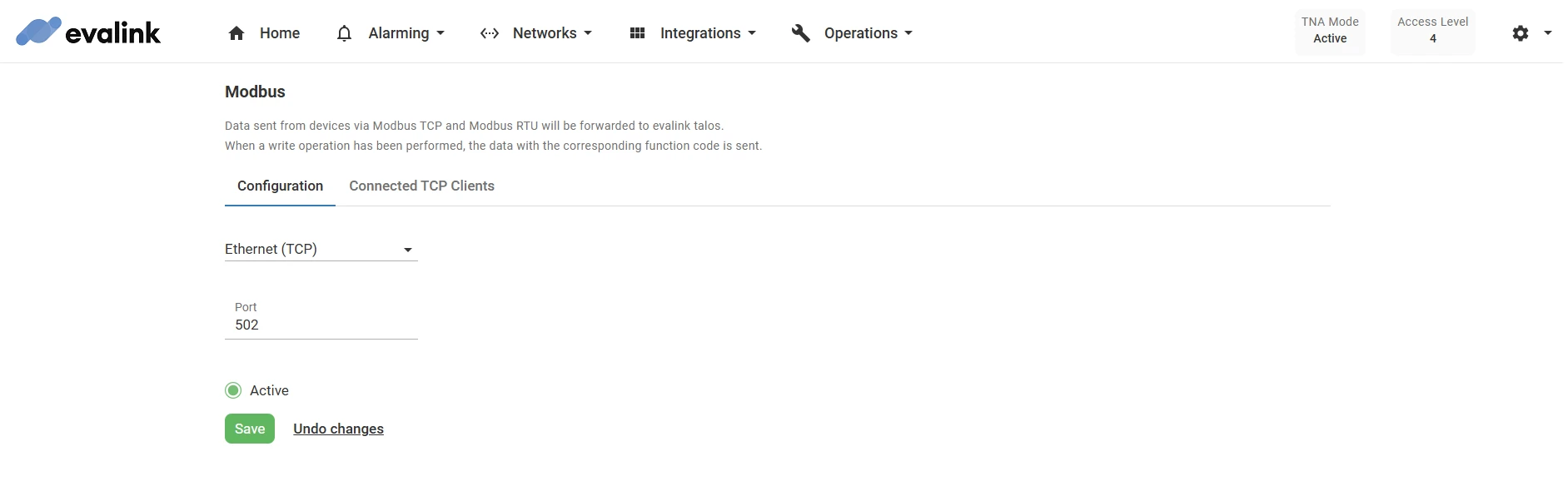
-
On the configuration page, you can choose either Ethernet Modbus TCP or Serial Port for Modbus RTU
-
Under Port, enter the port number for the connection
The default value is 502 and the port range: 10 - 32767
The TCP server supports no more than 5 simultaneous incoming connections.
-
Click on Save
-
(Optional) Click on Undo changes to reset the port number to the previous value
-
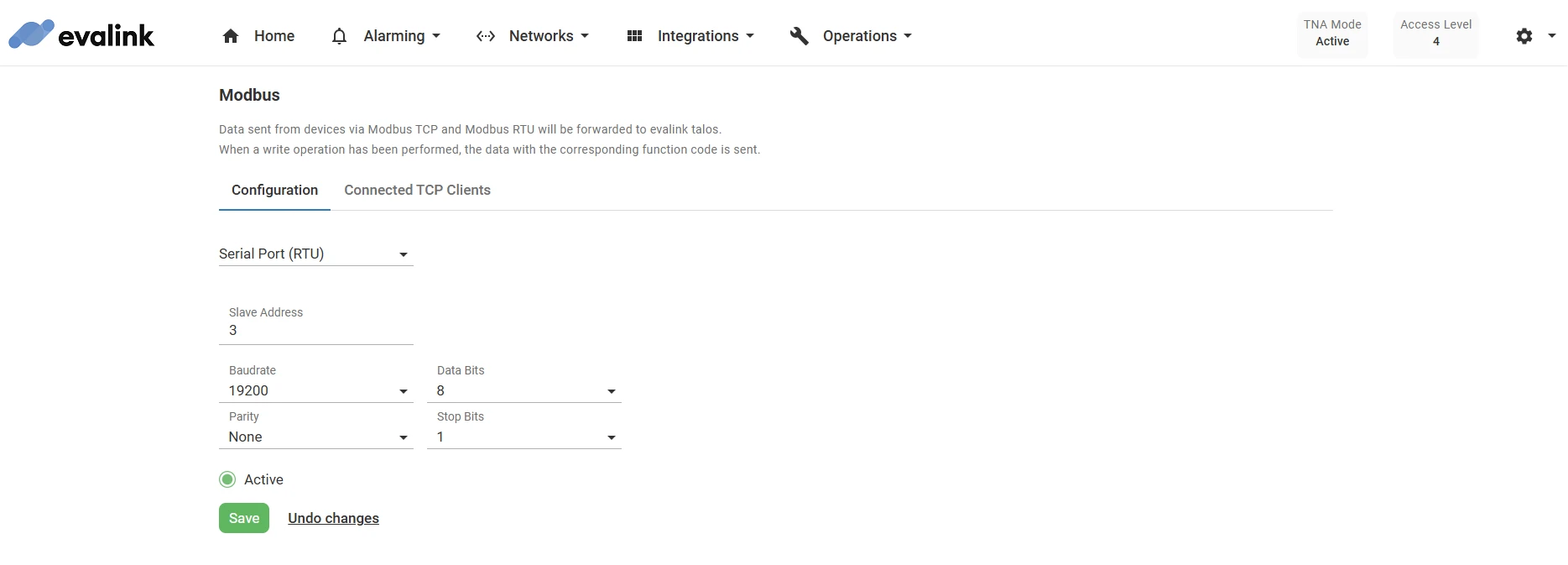
For Modbus RTU, choose Serial Port instead of Ethernet from the drop down menu, then configure the following settings:
Modbus RTU cannot be configured if the serial port is already used by another integration.
When the serial port disconnects during runtime, the server automatically restarts every 5 seconds until the connection is restored.
| Slave address | A unique identifier assigned to each device connected to the Modbus network. It ensures that the Modbus master device communicates with the intended device when sending commands or requesting data. The values range from 1 up to 247 Default value: 3 |
| Baudrate | The Baudrate is the speed at which data bits are sent. The values range from 300 up to 115200 Default value: 19200 |
| Data Bits | The Data Bits is the number of bits of data in each frame. Possible values are 7 and 8 Default value: 8 |
| Parity | The Parity bit can provide a simple form of error detection. Possible values are: None: no parity bit is added to the data. Even: the parity bit is set to space 0 if the total number of data bits in the mark 1 state is even. Odd: the parity bit is set to space 0 if the total number of data bits in the mark 1 state is odd. |
| Stop Bits | The Stop Bits is the number of bits used to mark the end of a frame. Possible values are 1 and 2 Default value: 1 |
-
Click on Save
-
(Optional) Click on Undo changes to reset the parameters to their previous values
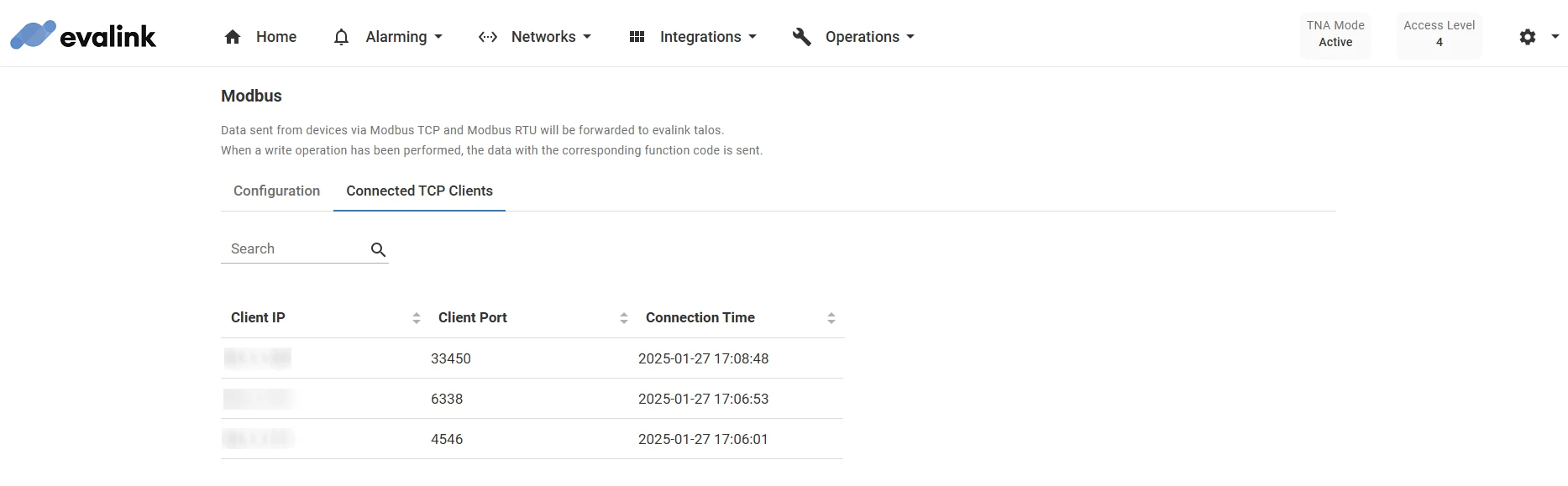
Connected Clients
On the Connected TCP Clients page, you can see a table with all connected clients over TCP. You can also search records by IP and Port fields.
The table supports sorting by columns. To sort, click on the arrows next to the corresponding column header.
Forwarded Messages
The following types of Modbus messages are forwarded to evalink talos:
| Write Single Coil | |
| Write Single Register | |
| Write Multiple Coils | |
| Write Multiple Registers | |
| Write File record | |
| Mask Write Register |
The messages are forwarded to evalink talos in a pre-defined JSON based format with the following data:
{
"source": {
"type": "type",
"unit_id": "unit_id",
"ip": "unit_ip"
},
"function_code": {
"description": "message_description",
"value": "message_type"
},
"address": {
"value": "value_address"
},
"value":"new_value",
"unit": "data_format"
}
| The connection type identifier: RTU or TCP | |
| The ID of the message sender (device), provided in the incoming message. Note: Available only when the type is TCP. | |
| The IP of the message sender (device), determined by the TNA. Note: Available only when the type is TCP. | |
| The description of the incoming message generated based on the incoming message type. | |
| The type of the message provided in the incoming message. | |
| The address of the value to be changed by the message. | |
| The new value to be assigned. | |
| The format of the data. The value is always hex. |
Message Examples
Write Single Coil
{
"source": {
"type": "TCP",
"unit_id": "123",
"ip": "192.168.10.20"
},
"function_code": {
"description": "Write Single Coil",
"value": "5"
},
"address": {
"value": "BF"
},
"value":"on",
"unit": "hex"
}
Write Single Holding Register
{
"source": {
"type": "RTU"
},
"function_code": {
"description": "Write Single Holding Register",
"value": "6"
},
"address": {
"value": "9C45"
},
"value":"257",
"unit": "hex"
}
Write Multiple Coils
{
"source": {
"type": "TCP",
"unit_id": "123",
"ip": "192.168.10.20"
},
"function_code": {
"description": "Write Multiple Coils",
"value": "0F"
},
"address": {
"value": "1B",
"count": "9"
},
"value":["on", "on", "off", "on", "off", "off", "off", "off", "on"],
"unit": "hex"
}
Write Multiple Holding Registers
{
"source": {
"type": "RTU"
},
"function_code": {
"description": "Write Multiple Holding Registers",
"value": "10"
},
"address": {
"value": "12",
"count": "2"
},
"value":["13", "42"],
"unit": "hex"
}
 Link is copied
Link is copied